1/10-1/16
📍Location: Burnaby, BC



Buy Smart!
Once upon a time, there was a shopkeeper named Tienty who ran a small store. He was well-known for selling good-quality items at honest prices. One day, a young man walked into his shop and said,
“Sir, I need the cheapest thing you have. I don’t have much money.”
Tienty thought for a moment and handed him an old knife.
“This knife is cheap, but it will break easily. If you still want it, take it.”
The young man, without much thought, bought the knife and left.
A few days later, the young man returned, upset.
“Sir, this knife broke so quickly! It was useless!”
Tienty smiled calmly and said,
“That’s the problem with buying something just because it’s cheap. It’s not worth it. What really matters is finding something that’s both cheap and good. Let me show you.”
He took the young man to the market and showed him sturdy, well-made items that didn’t cost much.
“The value of something isn’t in how little you pay, but in how well it works for you and how long it lasts.”
From that day on, the young man always looked for both quality and price before buying anything. His life became much easier and happier.
This story teaches us an important lesson, It’s not about buying the cheapest thing—it’s about buying something that’s cheap and good. That’s the smart way to shop!

T&T Supermarket is a popular destination across Canada for those seeking a unique shopping experience with a wide range of Asian groceries and household items. Originally founded by a Taiwanese company, T&T now offers products from China, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia. Loved by immigrants and local Canadians alike, it has become a go-to spot for high-quality, diverse Asian goods.
The P-NP problem is an unsolved problem in theoretical computer science regarding whether complexity classes P and NP are equivalent. In brief, it asks whether problems that can be verified quickly can also be solved quickly.
ex) Bubble sort has a polynomial of n(n-1)/2. It is a quadratic polynomial in terms of n.
non-deterministic Turing machineverified in polynomial time.ex) Subset problem requires only add operation if relying on lucky guess(non-deterministic), but if solved deterministically, it takes 2^n time. It takes exponential time, not polynomial time. As the input size increases, it increases exponentially
Hardest NP problem
When all NP problems can be reduced to a problem A in polynomial time, then that A is NP-hard
It is an NP-hard problem while also being an NP problem.
1. Cryptography:
Security of cryptography often ensured by the complexity of a computational task. if P = NP, Almost all passwords become unsafe. it means that even someone who doesn't know the password can find it in polynomial time. Although the question of what degree polynomial it will be remains, if it becomes a P problem, we can reduce the degree through research, so the current encryption system is easily collapsible.
2. Optimization:
Optimization problems can represent real-world problems like scheduling, routing, and resource allocation. If P = NP, then solving these problems efficiently would lead to significant improvements in industries like transportation, logistics, and finance.
hardware or software-based, that monitors all incoming and outgoing traffic based on a defined set of
security rules. It establishes a barrier between secured internal networks and untrusted outside networks,
such as the internet. The basic security functions are packet filtering and application proxy
1st Generation (Packet Filtering Firewall):
A packet-filtering firewall makes decisions based on each individual packet.
2nd Generation (Stateful Inspection Firewall):
A stateful inspection firewall can determine the connection state of a packet. It keeps track of the state of network connections traveling across it, such as TCP streams. Filtering decisions are not only based on defined rules but also on the packet's history in the state table.
3rd Generation (Application Layer Firewall):
An application layer firewall can inspect and filter packets on any OSI layer, up to the application layer. It has the ability to block specific content and recognize when certain applications and protocols are being misused.
Application layer firewalls are hosts that run proxy servers. A proxy firewall prevents the direct connection between either side of the firewall; each packet has to pass through the proxy. It can allow or block traffic based on predefined rules. It can also be used as a network address translator (NAT).
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
IP Addresses and Protocols:
Packet filters and stateful inspection firewalls use this type of filtering to limit access to specific services
Application protocol:
This type of filtering is used by a gateway that relays and monitors the exchange of information for specific application protocols.
User Identity:
This is for users who identify themselves with a secure authentication method.
Network Activity:
Manages access based on factors such as the time of the request, the frequency of requests, or other activity patterns.
Capabilities:
Limitations:
Network traffic can be either outgoing or incoming. Firewalls maintain distinct sets of rules for both cases.
Outgoing Traffic:
Egress filtering inspects outgoing network traffic and prevents users on the internal network from accessing the outside network. For example, social networking sites can be blocked in schools. Mostly, outgoing traffic originating from the server itself is allowed to pass, but it's always better to set a rule on outgoing traffic to achieve more security and prevent unwanted communication.
Incoming traffic:
Ingress filtering is a way to protect a network from outside attacks by checking incoming traffic. This traffic is usually one of three types: TCP, UDP or ICMP. Each type has a source and destination address, and TCP and UDP also have port numbers. ICMP uses a different way to identify the purpose of a packet, by using type codes instead of port numbers. The firewall treats incoming traffic differently from other traffic.
To plan and use a firewall effectively, you need to make sure it lets through the right kind of traffic. This includes things like address ranges, protocols, applications, and content types. To make this happen, you should use your organization's security risk assessment and policy to create a list of the kinds of traffic you need to support. Then, you can break that list down into more detail to figure out how to filter everything using the right kind of firewall setup.
Advanced security features provided by certain firewalls:
1. Host-based Firewalls: Host-based firewalls are software applications or suites of applications installed on each network node. They control each incoming and outgoing packet. Host-based firewalls are needed because network firewalls cannot provide protection inside a trusted network. Host firewalls protect each host from attacks and unauthorized access.
2. Network-based Firewalls: Network firewalls function on the network level, filtering all incoming and outgoing traffic across the network. They protect the internal network by filtering the traffic using rules defined on the firewall. A network firewall might have two or more network interface cards (NICs). A network-based firewall is usually a dedicated system with proprietary software installed.
By using vulnerabilities and tunneling, it is possible to bypass a firewall.
Unix was developed by Bell Labs(Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and Douglas Mcllroy) in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It is a multi-user operating system that provides protection from other users and protection for system services from users. Unix was designed as a simpler and faster alternative to Multics.
kernel and many processes, each running a program. The protection ring isolates the Unix kernel from the processes, and each process has its own address space.concept of files for all persistent system objects, such as secondary storage, I/O devices, network, and inter-process communication.user associated with the process. Access to files is limited by the process's identity.
root user is defined as the system principal and can access anything.kernel and root processes have full system access.DAC) system.Protection status:
Subjects:
/etc/passwd./etc/group.newgrp).Challenges:
protection than security. It assumes a non-malicious user and a trusted system by default.file permissions based on what is necessary for things to work. Unfortunately, this means that all user processes are granted full access, and services have unrestricted access. Furthermore, users can invoke setuid(root) processes with all rights, which means they must trust the system processes.root.crypt() to the password with stored salt./etc/shadow for that user./etc/passwd.The file's owner UID must be equal to the process's effective UID, and the file's group GID must be a member of the process's active group.
rootSetuid enables a user to escalate privileges and define the execution environment.files, which can be categorized into:
File permissions are divided into three categories: Owner, Group, and Others.
The three types of permissions are Read, Write, and Execute, represented by rwx
ex) chmod 644 file - owner can read/write, group, others can read only.
chmod is a command used to change the permissions of a file.chown is a command used to change the owner of a file.chgrp is a command used to change the group of a file.Chroot is a way to create a domain in which a process is confined. The process can only read and write within a filesystem subtree, which applies to all descendant processes. You can also carry file descriptors in a 'chroot jail'. Setting up requires great care because, unfortunately, chroot can trick its own system.
with a setuid program./tmp), giving it a filename used by a higher authority service, and ensuring that the service can access the file.Cryptography is a method of keeping information secret that has been around for more than 2500 years. It has always been a competition between those who create codes and those who break them. In the past, people used things like paper and ink, cryptographic engines, telegrams, and radio to do cryptography. Today, computers and digital communication are used for modern cryptography.
Secure communication is a way of protecting data from unauthorized access. It involves encryption and other measures to ensure data is securely transmitted between two or more parties. Encryption is scrambling data so that it can only be read by the intended recipient.
covered writing that hides the existence of a message. It depends on the secrecy of the method used.hidden writing that hides the meaning of a message. It depends on the secrecy of a short key, not the method used.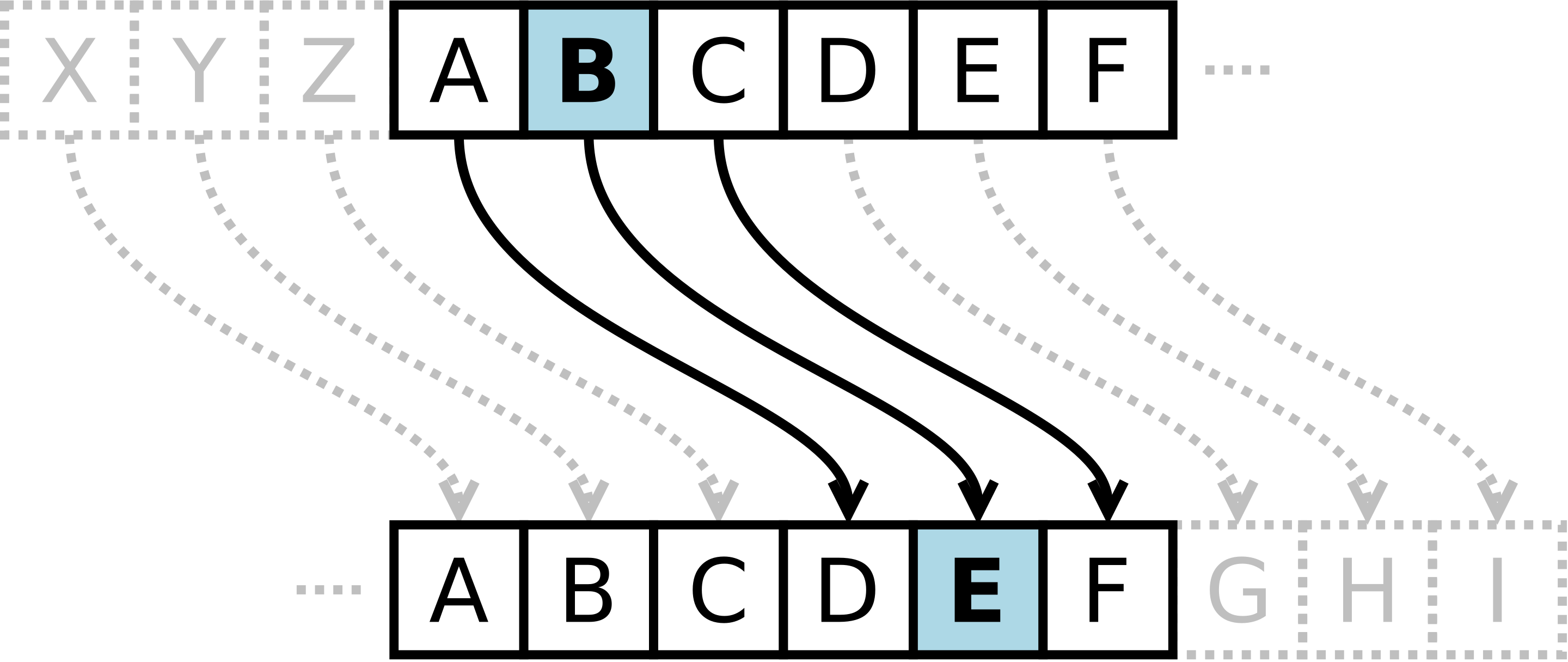
Encryption does not fully protect data from being changed by someone else. To make sure the data gets to its destination without being changed and to make sure it comes from a known source, we need something else.
A hash function maps a message of arbitrary length to an m-bit output.
Since a hash function is a many-to-one function, collisions can occur.
Hash functions are used for the following examples:
twice the key length of block ciphers due to the birthday attack.To fix these issues, you can:
SSL. However, AtE may not always be secure because the first step is decryption, which can reveal whether the decryption was successful or not.IPSec. Encryption alone may not be enough to ensure privacy. EtA is a secure option.SSH. However, the MAC method does not guarantee confidentiality.The most common public-key algorithm is called the RSA method, named after its inventors (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman). In this algorithm, the private key is a pair of numbers (N, d), and the public key is a pair of numbers (N, e). It should be noted that N is common to both the private and public keys.
Given a weighted graph and two vertices u and v, find a path of minimum total weight between u and v
applications:
single source on unweighted graph ⇒ just use BFS
This algorithm constructs the shortest path tree from a source node. It does not allow negative edge weights and is similar to Prim's algorithm. The algorithm employs a greedy strategy and has a complexity of O(|E| + |V|log|V|). It is widely used in various applications, such as artificial satellite GPS software. Since negative edges do not usually exist in the real world, Dijkstra's algorithm is one of the most suitable algorithms for practical use.
When all edge costs are positive, you can use Dijkstra's algorithm. However, if there are negative edges and negative cycles, a node with negative infinity occurs. In this case, you should use the Bellman-Ford algorithm. The Bellman-Ford algorithm can be used in situations involving negative edges and can detect negative cycles. The basic time complexity of the Bellman-Ford algorithm is O(VE), slower than Dijkstra's algorithm.
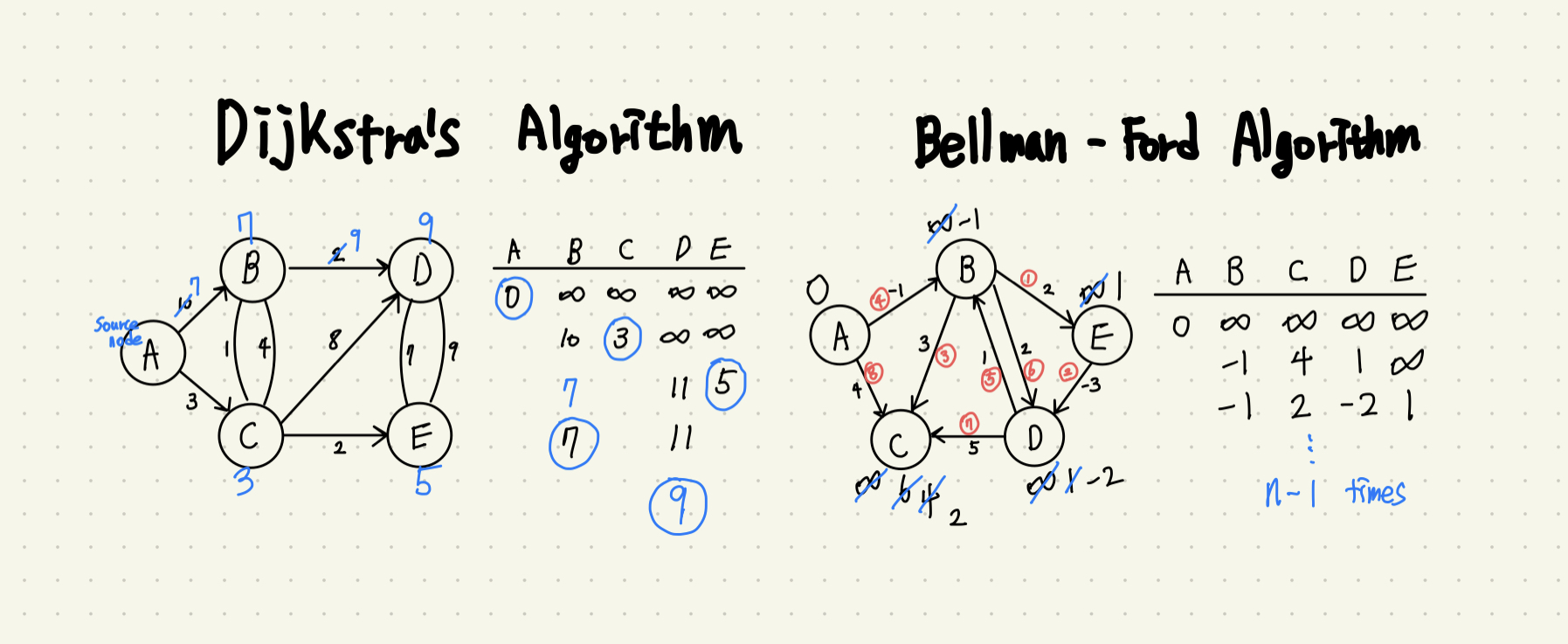
Dijkstra's and Bellman-Ford algorithms are algorithms that find the shortest path from one vertex to another when starting from a single vertex. However, if you want to find the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices, you need to use the Floyd-Warshall algorithm. While Dijkstra's algorithm chooses the least cost one by one, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm performs the algorithm based on the intermediate vertex.
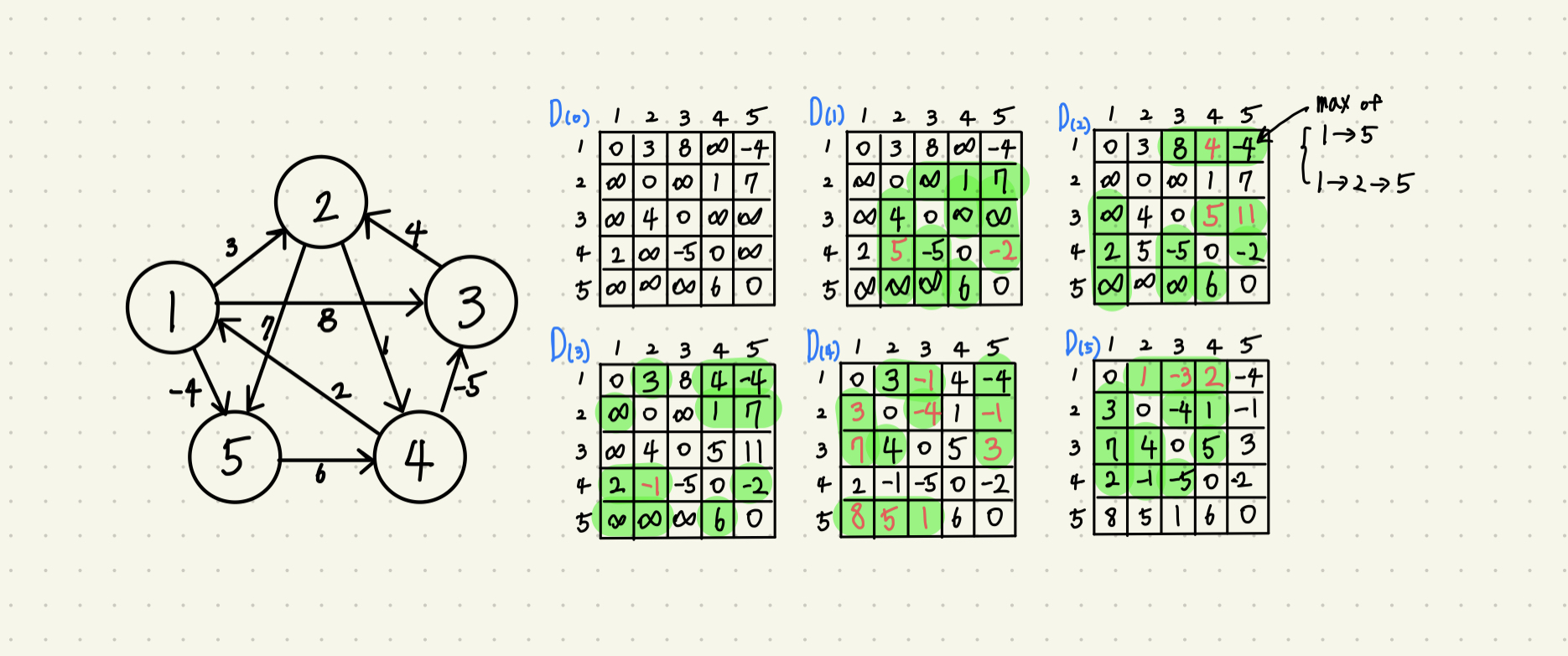
The green zone is a changeable area. Nodes with self-loops and containing intermediate vertices are not able to be changed.
The key idea of the Floyd-Warshall algorithm is to find the shortest distance based on the intermediate vertex. Calculate the number of cases where all n nodes are passed through.
The time complexity is O(V^3).